从零到精通 Hadoop 的系统学习文档
1) 学习路径总览(0→1→精通)
- 第 1 阶段(上手):理解架构,搭起本机伪分布式,能跑 WordCount、能用 HDFS 命令、能提交 YARN 任务。
- 第 2 阶段(好用):会写 MapReduce(或用 Spark 代替 MR),会用 Hive 做 SQL 数仓,会管理调度与权限,能处理 10–100GB 数据。
- 第 3 阶段(精通):搭建 3–5 节点集群,开启 HDFS/YARN 高可用、Kerberos;掌握数据分区/压缩/文件大小策略,能排查慢任务与数据倾斜,完成端到端数据管道。
2) 核心概念速读
- HDFS(分布式文件系统):一次写多次读;大文件切块(默认 128MB/256MB),NameNode 管理元数据,DataNode 存放块;复制因子(默认 3)。
- YARN(资源与任务调度):ResourceManager 分配资源,NodeManager 管理节点容器,ApplicationMaster 负责单个应用生命周期。
- MapReduce(批处理计算):Map 阶段并行处理切片,Shuffle 按 key 分发,Reduce 汇总。吞吐高、延迟高,适合批处理。
阿里云配置云服务器
1.配置专有网络和交换机
2.创建安全组,控制流量的入站
3.在阿里云创建ECS云服务器
1cpu,4g,node1
1cpu,2g,node2
1cpu,2g,node3
finalshell连接三个服务器
完成在阿里云服务器上设置主机名映射、JDK、SSH免密等基础配置
3) 快速上手实验(本机伪分布式)
目标:10–20 分钟在本机把 Hadoop 跑起来并成功执行一个任务。
3.1 环境准备
- 系统:macOS/Linux/WSL2 任意
- 安装:OpenJDK 11(
java -version验证) - 下载 Hadoop 3.3.x 并解压,设置环境变量:
export HADOOP_HOME=~/app/hadoop-3.3.x
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk # 以你的路径为准
export PATH=$HADOOP_HOME/bin:$HADOOP_HOME/sbin:$PATH
3.2 最小配置(伪分布式)
编辑 $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop 下 4 个文件(示例精简版):
core-site.xml
<configuration>
<property>
<name>fs.defaultFS</name><value>hdfs://localhost:9000</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hadoop.tmp.dir</name><value>/tmp/hadoop</value>
</property>
</configuration>
hdfs-site.xml
<configuration>
<property>
<name>dfs.replication</name><value>1</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.namenode.name.dir</name><value>file:///tmp/hadoop/nn</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.datanode.data.dir</name><value>file:///tmp/hadoop/dn</value>
</property>
</configuration>
yarn-site.xml
<configuration>
<property>
<name>yarn.nodemanager.aux-services</name><value>mapreduce_shuffle</value>
</property>
</configuration>
mapred-site.xml
<configuration>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.framework.name</name><value>yarn</value>
</property>
</configuration>
3.3 初始化并启动
hdfs namenode -format
start-dfs.sh
start-yarn.sh
jps # 看到 NameNode / DataNode / ResourceManager / NodeManager 即正常
3.4 验证 HDFS + 运行示例任务
hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /tmp/input
echo "hello hadoop hello bigdata" > /tmp/local.txt
hdfs dfs -put /tmp/local.txt /tmp/input/
# 运行自带 MapReduce 示例(WordCount)
hadoop jar $HADOOP_HOME/share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-*.jar wordcount \
/tmp/input /tmp/output
hdfs dfs -cat /tmp/output/part-r-00000 | head
4)常用命令速查
HDFS
# 查看根目录下的文件
hdfs dfs -ls /
# 在HDFS上创建/data/ods
hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /data/ods
# 把本地文件系统的local.csv上传到HDFS的/data/ods/
hdfs dfs -put local.csv /data/ods/
# 从HDFS下载到当前本地目录
hdfs dfs -get /data/ods/local.csv
# 在HDFS端串流输出文件内容到stdout,在用本地head截取前10行查看
hdfs dfs -cat /data/ods/local.csv | head
# 显示/data目录下每个条目的大小
hdfs dfs -du -h /data
# 递归删除HDFS路径/temp/output,跳过回收站直接删除
hdfs dfs -rm -r -skipTrash /temp/output
HDFS常用操作练习
echo 检查Hadoop环境
hdfs dfs -ls /
echo 在HDFS创建目录 /itcast/itheima
hdfs dfs -rm -r -skipTrach /itcast/itheima
hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /itcast/itheima
hdfs dfs -ls /itcast
echo 上传本机 /etc/hosts 到HDFS的 /itecast/itheima/
hdfs dfs -put -f /etc/hosts /itcast/itheima/
hdfs dfs -ls /itcast/itheima
echo 查看HDFS中刚上传的文件内容
hdfs dfs -cat /itcast/itheima/hosts | head -n 20
echo 把itheima加到文件最后一行
printf "itheima\n" | hdfs dfs -appendToFile - /itcast/itheima/hosts
echo 从HDFS下载该文件到本地指定目录
mkdir -p ~/itcast_lcoal
hdfs dfs -get -f /itcast/itheima/hosts ~/itcast_local/
ls -l ~/itcast_local/hosts
echo 在HDFS创建目录 /itcast/bigdata,并复制文件过去
hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /itcast/bigdata
hdfs dfs -cp /itcast/itheima/hosts /itcast/bigdata/
hdfs dfs -ls /itcast/bigdata
echo 把/itcast/itheima/hosts 重命名为 /itcast/itheima/myhost
hdfs dfs -mv /itcast/itheima/hosts /itcast/itheima/myhost
hdfs dfs -ls /itcast/itheima
echo 删除 /itcast 整个目录树
hdfs dfs -rm -r -skipTrach /itcast
hdfs dfs -ls /
5)HDFS存储原理
NameNode管理DataNode
文件切块与副本
- 大文件被切成 固定大小 Block;每个 Block 有 副本因子(replication factor,默认 3)。
- 放置策略(典型):1 副本在本机/本机架,另 1–2 个跨机架,兼顾局部性 + 容灾。
- Hadoop 3 支持 Erasure Coding(EC,纠删码),把 N 个数据片 + M 个校验片条带化,节省空间(相对 3 副本约省 50%+),但恢复/CPU开销更高,适合冷数据。
写入流程(Client → NN → DN 管道)
- Client 请求 NN 创建文件,NN 只做元数据检查、分配第一个 Block 的目标 DN 列表(考虑机架和负载)。
- Client 把数据按 packet 发送到 DN 管道(DN1→DN2→DN3 链式)。
- 校验:每个 DN 对 chunk 做校验和(CRC),管道逐级 ACK;Client 收到最后一个 DN 的 ACK 才算该段落持久化。
- Block 写满再申请下一个目标集合,直到文件关闭。
- 一致性模型:关闭(
hflush/hsync/close)前其它读者不可见;close 后原子可见。
读取流程(就近读取 + 并行)
- Client 向 NN 查询某文件的 块位置信息(只拿元数据)。
- 对每个 Block,Client 选择最近的 DN(优先同节点、同机架)读取;多个块可并发读。
- 读时进行 校验和验证;坏块会自动换读其它副本。
可靠性与自愈
- 心跳/块汇报:DN 定期向 NN 发心跳和 BlockReport,NN 维护块→副本位置的实时视图。
- 副本修复:NN 发现副本数不足(DN 掉线/坏块)会下发 复制命令 给其它 DN;多余副本会触发删副本。
- 重平衡(Balancer/Mover):均衡集群磁盘使用率、冷热层移动;集群再平衡属于在线后台作业。
- 安全模式(SafeMode):启动时 NN 等待达到阈值的块汇报才退出,防止仓促进行修复。
命名空间与持久化(fsimage/edits/检查点)
- fsimage:NN 的命名空间快照;edits:操作日志(增量)。
- 加载:启动时 NN 把 fsimage 载入内存并重放 edits 得到最新状态。
- 检查点(Checkpoint):定期把(fsimage+edits)合并,缩短重放时间(Hadoop 2 的 SecondaryNameNode,Hadoop 3 多用 Checkpoint/Standby NN)。
- NN 不存数据,失去 NN 即失去“地图”;因此用 HA + JournalNode 做强一致元数据复制。
一致性、权限与安全
- 近似 POSIX 语义:顺序写、仅支持追加(append);rename/close 提供原子性保证。
- 权限:类 Unix 权限 + ACL;企业常配 Kerberos 认证,传输或落盘可加密。
- 快照(Snapshot):低成本“只读时间点”视图,用于误删回滚与合规。
性能要点
- 数据本地性:计算移到数据附近(MapReduce/Spark),减少网络 IO。
- 大块/顺序 IO 友好:高吞吐、低随机写能力;小文件过多会压垮 NN 内存(每文件/块都有元数据)。
- 小文件问题:用 HAR/SequenceFile/Parquet 合并,或在上层用 HBase/Ozone、对象存储方案。
- 管道与批量:写入走 DN 管道、分包 ACK;读写均有预取与校验批处理。
复制 vs 纠删码(何时用)
- 复制(3x):写入快、恢复简单、读多快,热数据/在线作业优先。
- EC(如 RS-6-3):省空间,适合冷/归档,写入与恢复 CPU/网络成本更高。
fsck命令
echo 临时修改
hdfs dfs -setrep -R 2 /itcast/itheima
hdfs dfs -ls /itcast/itheima
hdfs fsck /itcast/itheima -files -blocks -racks
echo 检查某个文件的详细状态
hdfs fsck /itcast/itheima/hosts -files -blocks -locations
echo 检查某个HDFS的健康状态
hdfs fsck / -files -blocks -locations > fack_report.txt
echo 查看丢失或损坏的块
hdfs fsck / -list-corruptfileblocks
NameNode元数据
NameNode 里到底存了什么(in-memory 视图)
NameNode 常驻内存保存 命名空间与块索引 等元数据,典型包括:
- 命名空间(Namespace):目录树、文件/目录的 inode(名称、父子关系、创建/修改时间、权限、所有者、组、配额、快照标记、XAttrs、ACL 等)。
- 块映射(BlockMap):文件 → Block 列表(顺序、大小、是否 under-construction)。
- 块位置信息:每个 Block 的副本位于哪些 DataNode(由心跳/块汇报维护,不落盘,内存索引)。
- 租约/写锁(Leases):哪些客户端正在写哪些文件。
- 快照(Snapshots)与配额(Quotas):目录级存储/命名空间配额、快照差分信息。
- 存储策略与机架信息:如 HOT/WARM/COLD、EC/复制策略、机架拓扑。
- 安全与委托:权限、ACL、Delegation Tokens(如启用安全)。
直观理解:NameNode 记住“有哪些文件(目录树)、每个文件被切成哪些块、以及块副本目前在哪些 DN”。真正的数据块只在 DataNode 上。
持久化文件:fsimage 与 edits
NameNode 的持久化元数据由两类文件组成:
- fsimage:命名空间的快照文件(某一时刻的完整状态)。
- edits:操作日志(创建/删除/重命名/追加/权限变更等的增量事务)。
启动时流程:
- 读取最新 fsimage 到内存。
- 重放 edits(按事务 ID 递增)把状态追到最新。
- 生成新的 fsimage(Checkpoint),并截断旧的 edits(或滚动到新段)。
多数集群采用 QJM(Quorum Journal Manager):主/备 NN 都把 edits 同步写入 JournalNode 集群;Standby 定期合并并做 热备 Checkpoint。
6)MapReduce
分布式计算
分布式计算的两种工作模式
| 分散汇总 | “大家各算各的,再汇总结果”——强调并行与自治,典型于大规模数据聚合与流计算。 |
| 中心调度步骤执行 | “由指挥中心统一调度每一步”——强调顺序控制与全局可见,典型于批处理或复杂依赖任务。 |
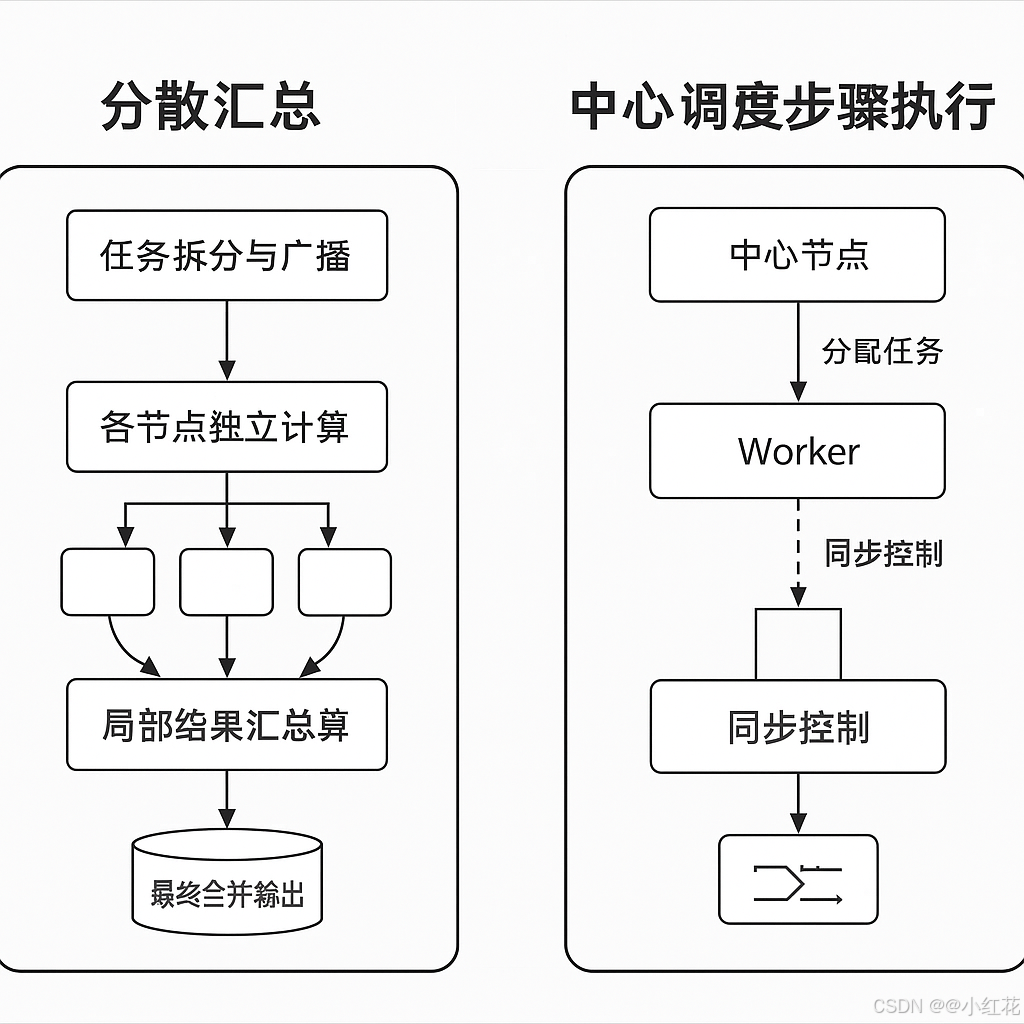
MapReduce一种分布式批处理编程模型与执行框架:把大数据计算拆成并行的 Map(映射) 和 Reduce(归并/聚合) 两阶段,中间由系统完成 Shuffle(按 key 分组、排序、拉取)。在 Hadoop 中,作业由 YARN 调度到各节点执行,具备容错与数据本地性。
7)YARN概述
ResourceManager管理NodeManager
YARN(Yet Another Resource Negotiator)是一个分布式资源管理系统,它是Hadoop生态系统中的重要组件之一。YARN的主要功能是管理和调度计算资源,确保在分布式计算环境中资源的高效利用。
YARN的核心架构组件
-
ResourceManager (RM):
-
功能:ResourceManager 是 YARN 的中央资源调度组件,负责全局的资源管理和资源调度。它有两个主要的子组件:
- Scheduler:根据资源需求和集群的可用资源来决定如何分配资源。Scheduler 不负责执行任务,它只根据需求进行资源的分配。Scheduler 会根据作业的优先级、资源需求等因素决定分配哪些资源给哪些任务。它支持多种调度策略,如容量调度器(CapacityScheduler)和公平调度器(FairScheduler)。
- ApplicationManager:负责管理和协调集群中所有应用的生命周期。它会处理应用程序的提交、启动、监控和失败恢复等工作。
-
-
NodeManager (NM):
-
功能:NodeManager 运行在每个工作节点(Node)上,负责管理本节点的资源使用情况。它的主要任务包括:
- 资源监控:监控节点上的资源使用情况(如 CPU、内存、磁盘、网络等)。
- 容器管理:NodeManager 会在本节点上启动和管理容器(Containers),并向 ResourceManager 报告本节点的状态。
- 任务执行:NodeManager 执行从 ResourceManager 分配给它的容器,容器内运行的任务将由 NodeManager 管理。
-
-
ApplicationMaster (AM):
- 功能:每个应用程序(例如 MapReduce 或 Spark 作业)都会有一个对应的 ApplicationMaster 运行在 YARN 中。ApplicationMaster 负责管理该应用程序的任务调度与资源申请,任务的执行以及失败重试等。每个 ApplicationMaster 向 ResourceManager 请求资源,在 NodeManager 上启动容器,并监控任务执行情况。
- 作用:ApplicationMaster 是应用的生命周期管理者,除了调度作业,还需要处理应用失败时的恢复。
-
Container:
- 功能:容器是 YARN 中分配的最小资源单元。当 ResourceManager 分配资源给某个应用程序时,它实际是分配了一些资源(例如 CPU、内存)给 NodeManager,在 NodeManager 上启动一个容器来执行任务。容器内可以运行应用的代码(如 MapReduce 任务或 Spark 任务),并在执行过程中使用容器中的资源。
- 管理:每个容器由 NodeManager 负责管理,NodeManager 监控容器的资源使用,确保容器在资源分配限制内运行。
YARN 的辅助架构组件
-
HistoryServer:
- 功能:HistoryServer 用于存储和展示作业执行历史数据。它提供了一个用户界面来查看已经完成的作业的执行情况、统计数据、日志文件等。尤其是在多个应用运行结束后,HistoryServer 能帮助用户追溯和分析作业的执行过程。
- 作用:在作业完成后,所有与作业相关的日志信息、作业元数据、执行结果等都可以被 HistoryServer 存储和访问。
- 工作流程:当一个应用程序完成时,ApplicationMaster 会将相关的历史信息上传到 HistoryServer。HistoryServer 根据这些信息生成可视化的作业历史记录,供用户查看。
-
ResourceManager 高可用性(HA):
- 功能:为了避免 ResourceManager 成为单点故障,YARN 提供了 ResourceManager 的高可用性架构。通过配置多个 ResourceManager 实例,确保当一个 ResourceManager 实例出现故障时,另一个实例能够接管任务,确保系统的高可用性。
- 作用:多个 ResourceManager 实例可以通过 Zookeeper 进行协调。在主 ResourceManager 宕机时,备份的 ResourceManager 会自动接管,保证集群的资源调度功能不间断。
-
NodeManager 高可用性(HA):
- 功能:NodeManager 也可以配置为高可用架构。当某个节点的 NodeManager 发生故障时,其他节点的 NodeManager 可以继续管理资源和容器的执行,确保集群的高可用性。
- 作用:通过监控和故障恢复机制,NodeManager 确保节点上运行的任务和资源管理不会因为单个 NodeManager 故障而中断。
-
Zookeeper:
- 功能:Zookeeper 是一个分布式协调工具,在 YARN 中用于确保各个组件的协调和管理。例如,Zookeeper 在 ResourceManager 高可用性架构中发挥重要作用,它帮助多个 ResourceManager 实例之间进行状态同步,确保系统中的各个组件能够共同协作。
- 作用:Zookeeper 用于存储和同步集群状态信息,确保整个集群在资源调度、作业管理等方面的协调性。
-
YARN Timeline Server:
- 功能:YARN Timeline Server 是用来存储和提供应用程序运行时的详细信息(如应用的生命周期、事件等)的服务。Timeline Server 主要用于支持 应用程序的监控和分析,例如,追踪每个作业的资源使用情况、任务状态变化等。
- 作用:提供作业的时间线信息,可以通过它追溯应用的执行过程,从而帮助管理员和开发者进行调优和故障排查。
-
YARN Application Client:
- 功能:YARN 的客户端是用户提交作业时与集群交互的接口。用户通过客户端向 ResourceManager 提交应用程序。客户端还可以查询作业的状态,查看作业的日志等。
- 作用:应用客户端帮助用户提交任务,并与集群中的其他组件交互。客户端负责与 ResourceManager 通信,启动 ApplicationMaster 并进行资源请求。
常用命令
echo 启动YARN资源管理器和节点管理器
start-yarn.sh
echo 停止YARN资源管理器和节点管理器
stop-yarn.sh
echo 查看YARN集群的状态
yarn top
echo 查看ResourceManager状态
yarn resourceManager
echo 查看NodeManager状态
yarn node -list
echo 提交一个YARN应用
yarn jar <your-application-jar> <main-class> <args>
echo 查看YARN作业的状态
yarn application -status <applicationId>
echo 查看所以运行中的作业
yarn application -list
echo 杀掉正在运行的作业
yarn application -kill <applicationId>
echo 查看某个作业的日志信息
yarn logs -applicationId <applicationId>
echo 查看容器信息
yarn container -list
echo 查看节点的容器列表
yarn node -containers <node-id>
echo 查看所有节点的状态
yarn node -list
echo 查看某个节点的详细信息
yarn node -status <node-id>
echo 刷新NodeManager
yarn rmadmin -refreshNodes
echo 查看资源的总体使用情况
yarn top
echo 查看YARN队列的状态
yarn queue -status
echo 查看ResourceManager高可用性状态
yarn rmadmin -getServiceState <rm-id>
echo 切换ResourceManager主备节点
yarn rmadmin -transitionToAction <rm-id>
8)Apache Hive
Apache Hive 是一个数据仓库工具,用于大规模数据存储和分析,基于 Hadoop 构建。它提供了一种类似 SQL 的查询语言(称为 HiveQL)来操作和查询存储在 Hadoop 分布式文件系统(HDFS)上的数据。Hive 最初由 Facebook 开发,用于简化 Hadoop 上大数据的处理与分析,后来成为 Apache 软件基金会的顶级项目。
Hive 提供了一种高层次的抽象,用户可以通过 SQL 语法查询和操作存储在 HDFS 中的数据,而不需要关心底层的 MapReduce 实现细节。
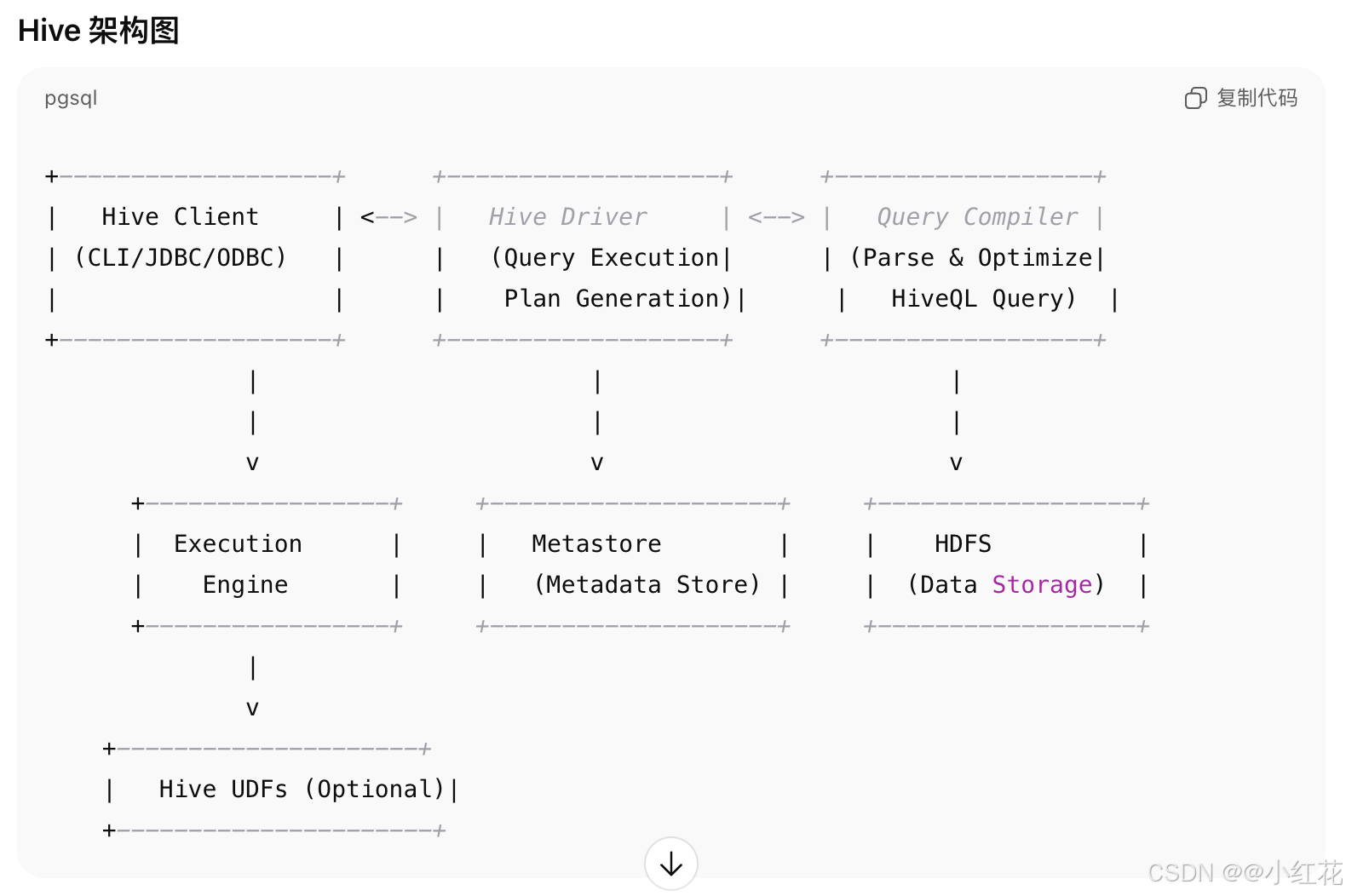
关键组件之间的关系
- Hive Client 提供了用户与 Hive 的交互界面(如 CLI、JDBC、ODBC 等)。
- Hive Driver 接收客户端请求并启动查询的生命周期管理。
- Query Compiler 将 HiveQL 查询转换为 MapReduce 任务或其他任务(如 Spark、Tez 等)。
- Metastore 存储了表的元数据(如列、分区等),并为查询优化提供元数据支持。
- Execution Engine 根据查询计划在 Hadoop 集群中执行查询。
- HDFS 提供分布式存储用于保存数据。
- Hive UDFs 用于扩展 Hive 的功能,处理自定义计算。
Hive常见命令
-- 查看所有数据库
show databases;
-- 查看当前数据库
select current_database();
-- 切换数据库
use mydb;
-- 查看所有表
show tables;
-- 查看表结构
describe employees;
-- 查看表数据
select * from employees limit 10;
-- 删除表
drop table employees;
-- 创建数据库
create database mydb;
-- 创建分区表
create table employees(id int,name string) paritioned by (department string);
-- 添加分区
alter table employees add partition(department='HR') location '/path/to/hdfs';
-- 加载数据到表
load data inpath '/path/to/data.csv' into table employees;
-- 执行查询
select name,age from employees where age > 30;
-- 创建视图
create view employees_above_30 as select name,age from employees where age > 30;
内部表
-
定义:内部表是由 Hive 完全控制的数据表。Hive 管理数据的生命周期,当删除内部表时,数据也会被删除。
-
特性:
- 数据存储在 Hive 的默认位置(通常是 HDFS 上的
user/hive/warehouse目录)。 - 删除内部表时,表数据和表结构都会被删除。
- 可以使用
CREATE TABLE创建。
- 数据存储在 Hive 的默认位置(通常是 HDFS 上的
create table employees (
id int,
name string,
age int,
department string
)
row format delimited
fields terminated by ','
stored as textfile;
外部表
-
定义:外部表指的是表的数据存储在 Hive 以外的地方,Hive 只是为其提供了结构和访问方式。数据存储的位置可以是 HDFS、HBase 或其他数据源。外部表的一个关键特性是删除表时,数据不会被删除。
-
特性:
- 外部表的数据通常存储在 Hive 默认路径之外,用户可以指定路径。
- 删除外部表时,Hive 只会删除表的元数据,而不会删除数据。
- 外部表适合需要与其他系统共享数据,或者希望不受 Hive 管理的情况下访问数据的场景。
create external table employees_external (
id int,
name string,
age int,
department string
)
row format delimited
fields terminated by ','
stored as textfile
location '/user/hive/warehouse/employees_data';
分区表
-
定义:分区表是一种根据某个列的值将数据分割存储的表。分区将数据按列的值(如日期、地区等)划分为多个子目录,通常用于提高查询性能。
-
特性:
- 分区表通过将数据分割成多个部分来提高查询效率,尤其是针对某些特定条件(如日期)进行筛选的查询。
- 每个分区在物理上是一个子目录,数据按分区字段的不同值存储在不同的目录中。
- 分区字段不能用于计算或包含空值,通常是离散的分类数据。
create table employees_partitioned (
id int,
name string,
age int
)
partitioned by (department string)
row format delimited
fields terminated by ','
stored as textfile;
-- 添加数据到特定分区
alter table employees_partitioned add partition (department='HR')
location '/user/hive/warehouse/employees/HR';
分桶表
-
定义:分桶表是通过对某个列(通常是主键或某些离散字段)进行哈希分桶的方式将数据存储在不同的文件中。每个桶(文件)存储的是该列值的某个子集,常用于提高查询效率,尤其是处理大规模数据时。
-
特性:
- 数据会根据指定的列进行哈希分桶,生成多个文件(桶)。
- 分桶可以帮助优化某些操作,如
JOIN、GROUP BY等,尤其是当查询涉及到分桶列时。 - 支持分桶存储在多个文件中,类似于数据库中的分区。
create table employees_bucketed (
id int,
name string,
age int
)
clustered by (id) into 4 buckets
row format delimited
fields terminated by ','
stored as textfile;
导入数据到Hive
使用load data语句将数据从本地文件系统获HDFS中加载到Hive表中。
1、从本地文件系统导入数据
load data local inpath '/local/path/to/datafile' into table your_table;
2、从HDFS导入数据
load data inpath '/hdfs/path/to/datafile' into table your_table;
3、从Hive表中选择数据并插入到另一个表
insert into table target_table select * from source_table;
从Hive导出数据
1、导出到HDFS中的指定目录
insert overwrite directory '/hdfs/path/to/output_dir'
row format delimited
fields terminated by ','
select * from your_table;
2、使用hive -e命令将查询结果导出到文件系统
hive -e "select * from your_table" > /local/path/to/output_file
Hive修改表的常见操作
-- 修改表名
alter table old_table_name renamne to new_table_name;
alter table employees rename to employee_data;
-- 添加列
alter table table_name add columns(new_column_name data_type);
alter table employees add columns(salary double);
-- 删除列
alter table table_name replace columns(column_name data_type, ...);
alter table employees replace columns(id int, name string, department string);
-- 修改列的数据类型
alter table table_name change column old_column_name new_column_name new_data_type;
alter table employees change column age age bigint;
-- 修改表的存储格式
alter table table_name set fileformat new_file_format;
alter table employees set fileformat orc;
-- 修改表的存储位置
alter table table_name set location 'new_location';
alter table employees set location '/user/hive/warehouse/new_employees_data/'
-- 修改表的表属性
alter table table_name set tblproperties('property_name'='value');
alter table employees set tblproperties('compression'='snappy');
-- 添加分区
alter table table_name add partition (partition_spec) [location 'path'];
alter table employees_partitioned add partition (year-2021, month=12) location '/user/hive/warehhouse/employees/2021/12';
-- 删除分区
alter table table_name drop partition (partition_spec);
alter table employees_partitioned drop partition(year=2020, month=06);
复杂类型array数组
-- 创建包含array的表
create table student_scores (
student_id int,
student_name string,
scores array<int>
);
-- 插入数据
insert into student_scores values
(1, 'jack', array(80,90,100)),
(2, 'alice', array(95,60,40)),
(3, 'bob', array(75,90,80));
-- 查询整个array
select student_id, student_name, scores
from student_scores;
-- 获取array中的特定元素:使用scores[0]获取数组的第一个元素
select student_id,student_name,scores[0] as first_score
from student_scores;
-- 使用size()函数获取数组的长度
select student_id, student_name, size(scores) as num_scores
from student_scores;
-- 获取array的子集:使用slice()函数可以获取数组的指定范围
select student_id, student_name, slice(scores, 1, 2) as first_two_scores
from student_scores;
-- 数组拼接:将两个array合并为一个array
select student_id, concat(scores, array(95, 98)) as all_scores
from student_scores;
-- 查找元素:检查数组是否包含某个特定的元素
select student_id, array_contains(scores, 90) as has_score_90
from student_scores;
-- 数组去重:返回数组中不重复的元素
select student_id, array_distinct(scores) as distinct_scores
from student_scores;
复杂类型map映射
-- 创建包含map的表
create table student_scores (
student_id int,
student_name string,
scores map<string, int>
);
-- 插入数据
insert into student_scores values
(1, 'jack', map('math', 80, 'english', 90, 'history', 89)),
(2, 'alice', map('math', 80, 'english', 90, 'history', 89)),
(3, 'bob', map('math', 80, 'english', 90, 'history', 89));
-- 查询整个map
select student_id, student_name, scores
from student_scores;
-- 查询map中的特定值
select student_id, student_name, scores['math'] as math_score
from student_scores;
-- 使用size函数获取map中键值对的数量
select student_id, student_name, size(scores) as num_courses
from student_scores;
-- 使用map_keys()和map_values()获取所有键或值
select student_id, student_name, map_keys(scores) as course_names
from student_scores;
-- 检查map是否包含某个键
select student_id, student_name, map_contains_key(scores, 'math') as has_math_score
from student_scores;
复杂类型struct结构
-- 创建包含struct的表
create table student_info(
student_id int,
student_name string,
student_info struct<name:string, age:int, gender:string>
);
-- 插入数据
insert into student_info values
(1, 'John', struct('John', 20, 'Male')),
(2, 'alice', struct('alice smith', 22, 'Male')),
(3, 'bob', struct('bob jognson', 23, 'Male'));
-- 查询整个struct
select student_id, student_name, student_info
from student_info;
select student_id, student_name, student_info.name as student_name
student_info.age as student_age, student_info.gender as student_gender
from student_info;
-- 使用struct存储嵌套数据
create table student_courses(
student_id int,
student_name string,
courses array<struct<course_name:string, score:int, credits:int>>
);
-- 使用struct进行数据转换
select student_id, student_name
named_struct('course_name', 'math', 'score', 95, 'credits', 3) as math_course_info
from student_courses;
操作
-- RLIKE 正则表达式匹配
select * from table_name where column_name rlike 'pattern';
select * from users where email rlike 'gmail';
-- TABLESAMPLE 数据抽样
select * from table_name tablesample(bernoulli|system) percent n;
-- 抽10%的数据
select * from sales tablesample(bernoulli) percent 10;
-- 虚拟列。total_price就是
select order_id, quantity, unit_price, (quantity * unit_price) as total_price from orders;
-- 将所有名字转化成大写并且连接一个字符串
select concat(upper(name), '- employee') from employees;
-- 将日期格式化为YYYY-MM-DD形式
select date_format(event_date, 'yyyy-MM-dd') from events;
-- 条件判断
select name,
case
when score >= 60 then 'Pass'
else 'Fail'
end as result
from students;
-- 条件
select if(score >= 60, 'Pass', 'Fail') from students;
-- 返回第一个非空值
select coalesce(nickname, 'Anonymous') from users;
-- 如果两个值相等,则返回NULL,否则返回第一个值
select nullif(price, 0) from products;
案例
聊天平台每天都会有大量的用户在线,会出现大量的聊天数据,通过对聊天数据的统计分析,可以更好的对用户构建精准的用户画像,为用户提供更好的服务以及实现高ROI的平台运营推广,给公司的发展决策提供精确的数据支撑我们将基于一个社交平台App的用户数据,完成相关指标的统计分析并结合BI工具对指标进行可视化展现。
需求分析
需求
统计今日总消息量
create table db_msg.tb_rs_total_msg_cnt comment '每日消息总量' as
select msg_day, count(*) as total_msg_cnt from db_msg.tb_msg_etl group by msg_day;
统计今日每小时消息量、发送和接收用户数
create table db_msg.tb_rs_hour_msg_cnt comment '每小时消息量趋势' as
select
msg_hour,
count(*) as total_msg_cnt,
count(distinct sender_account) as sender_user_cnt,
count(distinct receiver_account) as receiver_user_cnt
from db_msg.tb_msg_etl
group by msg_hour;
统计今日各地区发送消息数据量
create table db_msg.tb_rs_loc_cnt comment '每日各地区发送消息总量' as
select
msg_day, sender_lng, sender_lat, count(*) as total_msg_cnt
from db_msg.tb_msg_etl
group by msg_day, sender_lng, sender_lat;
统计今日发送消息和接收消息的用户数
create table db_msg.tb_rs_user_cnt comment '每日发送和接收消息的人数' as
select
msg_day,
count(distinct sender_account) as sender_user_cnt,
count(distinct receiver_account) as receiver_user_cnt
from db_msg.tb_msg_etl
group by msg_day;
统计今日发送消息最多的Top10用户
create table db_msg.tb_rs_s_user_top10 comment '发送消息最多的10歌用户' as
select
sender_name,
count(*) as sender_msg_cnt
from db_msg.tb_msg_etl group by sender_name
order by sender_msg_cnt desc
limit 10;
统计今日接收消息最多的Top10用户
create table db_msg.tb_rs_r_user_top10 comment '接收消息最多的10个用户' as
select
receiver_name,
count(*) as receiver_msg_cnt
from db_msg.tb_msg_etl group by receiver_name
order by receiver_msg_cnt desc
limit 10;
统计发送人的手机型号分布情况
create table db_msg.tb_rs_sender_phone comment '发送人的手机型号分布' as
select
sender_phonetype,
count(*) as cnt
from db_msg.tb_msg_etl group by sender_phonetype;
统计发送人的设备操作系统分布情况
create table db_msg.tb_rs_sender_os comment '发送人的os分布' as
select
sender_os,
count(*) as cnt
from db_msg.tb_msg_etl group by sender_os;
建立数据库,建立表格
-- 建立数据库,建立表格
drop database if exists db_msg cascade;
create database db_msg;
use db_msg;
show databases;
--如果表已存在就删除
drop table if exists db msg.tb_msg_source:
--建表
create table db msg.tb msg source(
msg_time string comment“消息发送时间",
sender name string comment"发送人昵称",
sender_account string comment“发送人账号",
sender_sex string comment"发送人性别",
sender_ip string comment "发送人ip地址",
sender_os string comment "发送人操作系统",
sender_phonetype string comment"发送人手机型号",
sender_network string comment"发送人网络类型",
sender_gps string comment"发送人的GPS定位",
receiver_name string comment"接收人昵称",
receiver_ip string comment"接收人IP",
receiver_account string comment“接收人账号",
receiver_os string comment"接收人操作系统",
receiver_phonetype string comment"接收人手机型号",
receiver_network string comment“接收人网络类型",
receiver_gps string comment"接收人的GPS定位",
receiver_sex string comment"接收人性别",
msg_type string comment"消息类型",
distance string comment"双方距离",
message string comment“消息内容
);
数据清洗
-- 问题
-- Some data fields are empty, which means the data is not valid.
select
msg_time,
sender_name,
sender_gps
from db_msg.tb_msg_scource
where length(sender_gps) = 0
limit 10;
-- We need to count the number of messages per day and per hour, but the data only has an overall time field and no day or hour fields, which makes it difficult to process.
select
msg_time
from db_msg.tb_msg_source
limit 10;
-- We need to build a visual map of the region using longitude and latitude, but the GPS longitude and latitude data is only one field.
select
msg_time,
sender_name,
sender_gps
from db_msg.tb_msg_scource
where length(sender_gps) = 0
limit 10;
-- 需要统计每天、每个小时的消息量,但是数据没有天和小时字段,只有整体时间字段,不好处理
select
msg_time
from db_msg.tb_msg_source
limit 10;
-- 需要对经度和纬度构建地区的可视化地图,但是数据中 GPS 经纬度为一个字段
select
msg_time,
sender_name,
sender_gps
from db_msg.tb_msg_scource
where length(sender_gps) = 0
limit 10;
-- We need to count the number of messages per day and per hour, but the data only has an overall time field and no day or hour fields, which makes it difficult to process.
select
msg_time
from db_msg.tb_msg_source
limit 10;
-- We need to build a visual map of the region using longitude and latitude, but the GPS longitude and latitude data is only one field.
select
msg_time,
sender_name,
sender_gps
from db_msg.tb_msg_scource
where length(sender_gps) = 0
limit 10;
-- 需要统计每天、每个小时的消息量,但是数据没有天和小时字段,只有整体时间字段,不好处理
select
msg_time
from db_msg.tb_msg_source
limit 10;
-- 需要对经度和纬度构建地区的可视化地图,但是数据中GPS经纬度为一个字段
select
sender_gps
from db_msg.tb_msg_source
limit 10;
-- 解决方案
-- 对字段为空的不合法数据进行过滤
-- 通过时间字段构建天和小时字段
-- 从GPS的经纬度中提取经度和纬度
-- 将ETL以后的结果保存到一张新的Hive表中
insert overwrite table db_msg.tb_msg_etl
select
*,
date(msg_time) as msg_day,
hour(msg_time) as msg_hour,
split(sender_gps, ',')[0] as sender_lng,
split(sender_gps, ',')[1] as sender_lat
from db_msg.tb_msg_source
where length(sender_gps) > 0;